Specifically, fixed overhead variance is defined as the difference between Standard Cost and fixed overhead allowed for the actual output achieved and the actual fixed overhead cost incurred. The fixed factory overhead variance represents the difference between the actual fixed overhead and the applied fixed overhead. The other variance computes whether or not actual production was above or below the expected production level. Recall that the standard cost of a product includes not only materials and labor but also variable and fixed overhead. It is likely that the amounts determined for standard overhead costs will differ from what actually occurs.
Fixed Overhead Variance Journal Entry
Hopefully, by the end of the year there will be enough good aprons produced to absorb all of the fixed manufacturing overhead costs. In a standard costing accounting system, the fixed overhead variance is the 2 2 perpetual v. periodic inventory systems financial and managerial accounting difference between the standard fixed overhead and the actual fixed overhead. To operate a standard costing system and allocate fixed overhead, the business must first decide on the basis of allocation.
AccountingTools
The fixed overhead production volume variance is favorablebecause the company produced and sold more units thananticipated. In a standard cost system, overhead is applied to the goods based on a standard overhead rate. The standard overhead rate is calculated by dividing budgeted overhead at a given level of production (known as normal capacity) by the level of activity required for that particular level of production. The credit balance on the fixed overhead budget variance account (2,000), has now been split between the work in process inventory account (600) and the cost of goods sold account (1,400) decreasing both accounts by the appropriate amount. The debit balance on the fixed overhead volume variance account (1,040) has been charged to the cost of goods sold account, and both variance account balances have been cleared.
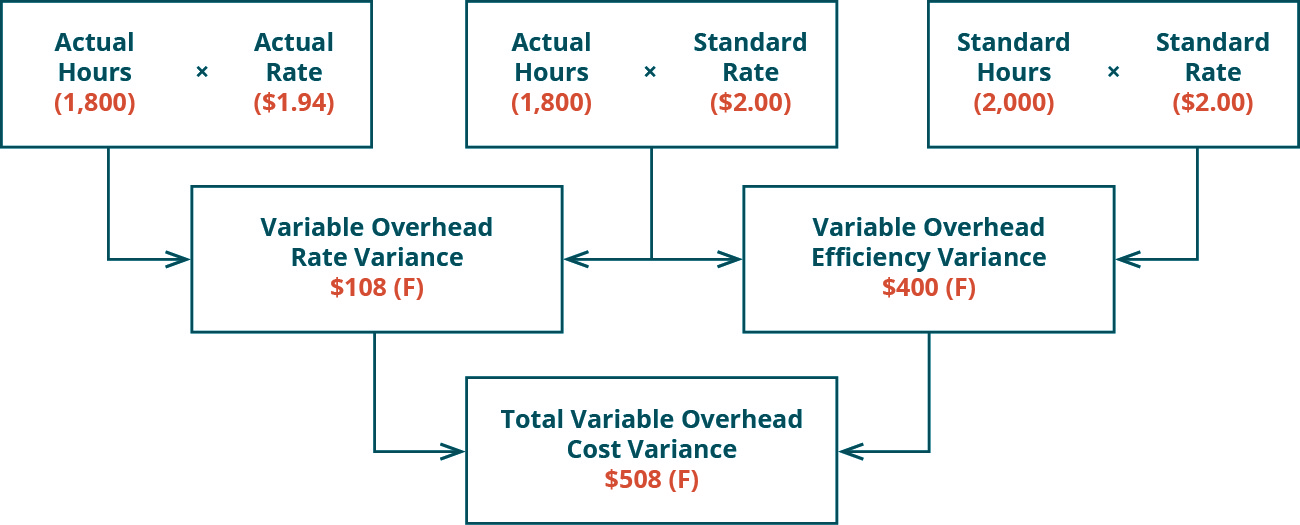
Variable Overhead Spending Variance
This is the portion of volume variance that is due to the difference between the budgeted output efficiency and the actual efficiency achieved. Sometimes these flexible budget figures and overhead rates differ from the actual results, which produces a variance. For example, the production department of Tahkila Industrials expects that the annual fixed overheads of the company will be $500,000 for the year ended 2019.
- A favorable variance means that the actual variable overhead expenses incurred per labor hour were less than expected.
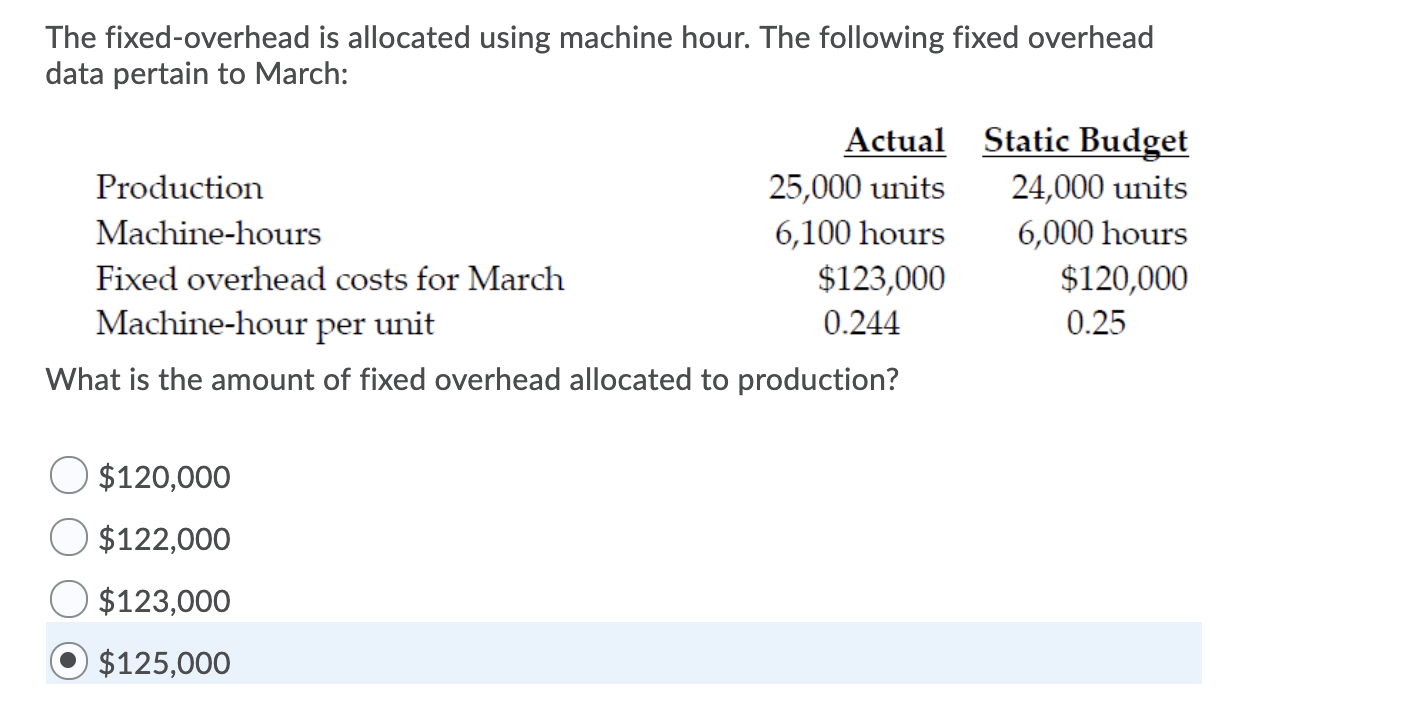
- We begin by determining the fixed manufacturing overhead applied to (or absorbed by) the good output produced in the year 2023.
- Controlling overhead costs is more difficult and complex than controlling direct materials and direct labor costs.
After the reasons have been highlighted the company takes measures to deal with any material variances throughout the year to minimize costs. In such a case, the company incurs an entirely new expense that the production department didn’t anticipate. This variance arises due to the difference in the number of working days when the actual number of working days is greater than standard working days.
This is due to the actual production volume that it has produced in August is 50 units lower than the budgeted one. We begin by determining the fixed manufacturing overhead applied to (or absorbed by) the good output produced in the year 2023. Recall that we apply the overhead costs to the aprons by using the standard amount of direct labor hours. A simple way to assign or allocate the fixed costs is to base it on things such as direct labor hours, machine hours, or pounds of direct material. Accountants realize that this is simplistic; they know that overhead costs are caused by many different factors. Nonetheless, we will assign the fixed manufacturing overhead costs to the aprons by using the direct labor hours.
We take the difference between the actual number of units produced and the estimated number of units produced. Hence, any significant increase or decrease in fixed cost is a critical point for an entity and shall be dealt with immediately since an unexpected material expense would hurt the company’s financial statements. A favorable variance may occur due to economies of scale, bulk discounts for materials, cheaper supplies, efficient cost controls, or errors in budgetary planning.
Specifically, fixed overhead variance is defined as the difference between standard cost and fixed overhead allowed for the actual output achieved and the actual fixed overhead cost incurred. To determine the overhead standard cost, companies prepare a flexible budget that gives estimated revenues and costs at varying levels of production. The standard overhead cost is usually expressed as the sum of its component parts, fixed and variable costs per unit. Note that at different levels of production, total fixed costs are the same, so the standard fixed cost per unit will change for each production level. However, the variable standard cost per unit is the same per unit for each level of production, but the total variable costs will change. This is a cost that is not directly related to output; it is a general time-related cost.
Fixed Overhead Expenditure Variance, also known as fixed overhead spending variance, is the difference between budgeted and actual fixed production overheads during a period. As an example of an unfavorable fixed overhead spending variance, a passing tornado delivers a glancing blow to the production facility of Hodgson Industrial Design, resulting in several hundred roofing tiles being blown off. This cost is part of the facilities maintenance budget, which normally does not vary much from month to month, and so is part of the company’s fixed overhead.
